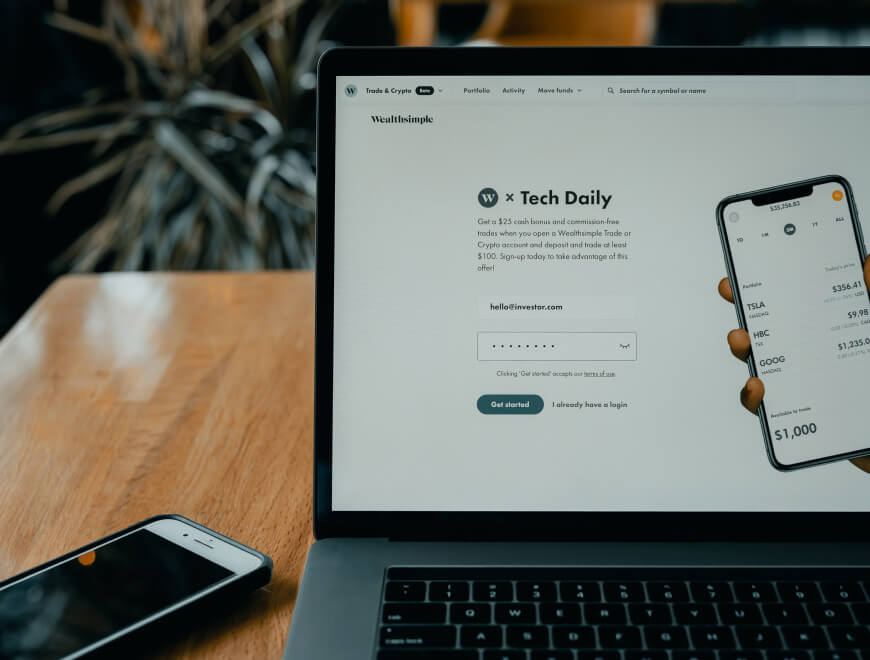
In today's financial landscape, maintaining a healthy credit score is paramount. Whether you're applying for a mortgage, seeking a loan, or even pursuing certain job opportunities, your creditworthiness can significantly impact your financial future. However, for those grappling with less-than-stellar credit, the prospect of repairing it can seem daunting. Enter the Credit Repair Organizations Act …
Understanding the Credit Repair Organizations Act (CROA): Your Guide to Credit Repair
In today’s financial landscape, maintaining a healthy credit score is paramount. Whether you’re applying for a mortgage, seeking a loan, or even pursuing certain job opportunities, your creditworthiness can significantly impact your financial future. However, for those grappling with less-than-stellar credit, the prospect of repairing it can seem daunting. Enter the Credit Repair Organizations Act (CROA), a crucial piece of legislation designed to protect consumers seeking assistance with credit repair. In this blog post, we’ll delve into what the CROA entails, how it safeguards consumers, and what you need to know before engaging with credit repair organizations.
Understanding the Credit Repair Organizations Act (CROA): Enacted in 1996, the Credit Repair Organizations Act (CROA) is a federal law aimed at regulating the credit repair industry and safeguarding consumers from deceptive or fraudulent practices. Its primary objective is to ensure transparency, fairness, and accuracy in credit repair services provided by organizations or companies.
Key Provisions of the CROA:
- Disclosure Requirements: Under the CROA, credit repair organizations are mandated to provide consumers with a written contract detailing the terms and conditions of their services. This contract must include information such as the total cost of services, a description of the services to be rendered, the duration of the contract, and the consumer’s rights under the law.
- Prohibited Practices: The CROA prohibits certain practices that are deemed unfair or deceptive. For instance, credit repair organizations are barred from making false or misleading statements about a consumer’s creditworthiness or promising specific outcomes, such as guaranteed credit score improvement.
- Right to Cancel: Consumers have the right to cancel their contract with a credit repair organization within three business days of signing it, without incurring any penalty or obligation.
- Fee Restrictions: The CROA limits the fees that credit repair organizations can charge consumers before services are rendered. These organizations cannot demand payment until they have completed the promised services.
- Written Examination of Credit Report: Credit repair organizations must provide consumers with a written examination of their credit report and identify any items that are inaccurate, incomplete, or outdated. They must also inform consumers of their right to dispute erroneous information directly with credit reporting agencies.
Consumer Protections Under the CROA: The CROA provides several protections to consumers seeking credit repair assistance:
- Right to Legal Recourse: Consumers who believe that a credit repair organization has violated the CROA have the right to pursue legal action and seek damages.
- Regulatory Oversight: The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) oversees compliance with the CROA and takes enforcement actions against violators. Consumers can report violations to the FTC for investigation.
- Education and Awareness: The CROA aims to educate consumers about their rights and responsibilities when dealing with credit repair organizations, empowering them to make informed decisions.
Tips for Choosing a Reputable Credit Repair Organization:
- Research Extensively: Before engaging with a credit repair organization, research its reputation, credentials, and track record. Look for reviews from past clients and check for any complaints filed with the FTC or Better Business Bureau (BBB).
- Beware of Red Flags: Exercise caution if a credit repair organization makes lofty promises or demands payment upfront before rendering services. Legitimate organizations adhere to the provisions of the CROA and prioritize transparency and integrity.
- Understand Your Rights: Familiarize yourself with the rights afforded to you under the CROA, including the right to cancel a contract within three business days and the right to dispute inaccurate information on your credit report.
Conclusion: The Credit Repair Organizations Act (CROA) serves as a crucial safeguard for consumers seeking assistance with credit repair. By understanding its provisions and protections, consumers can make informed decisions when engaging with credit repair organizations. Remember to conduct thorough research, exercise caution, and assert your rights under the law. With diligence and awareness, you can navigate the credit repair process with confidence and work towards achieving financial stability.